Introduction
Shallow copy and deep copy are fundamental concepts in programming, especially when working with objects, arrays, and memory references. Misunderstanding them often leads to bugs, unexpected data mutation, and performance issues. This article explains both concepts clearly with practical examples.
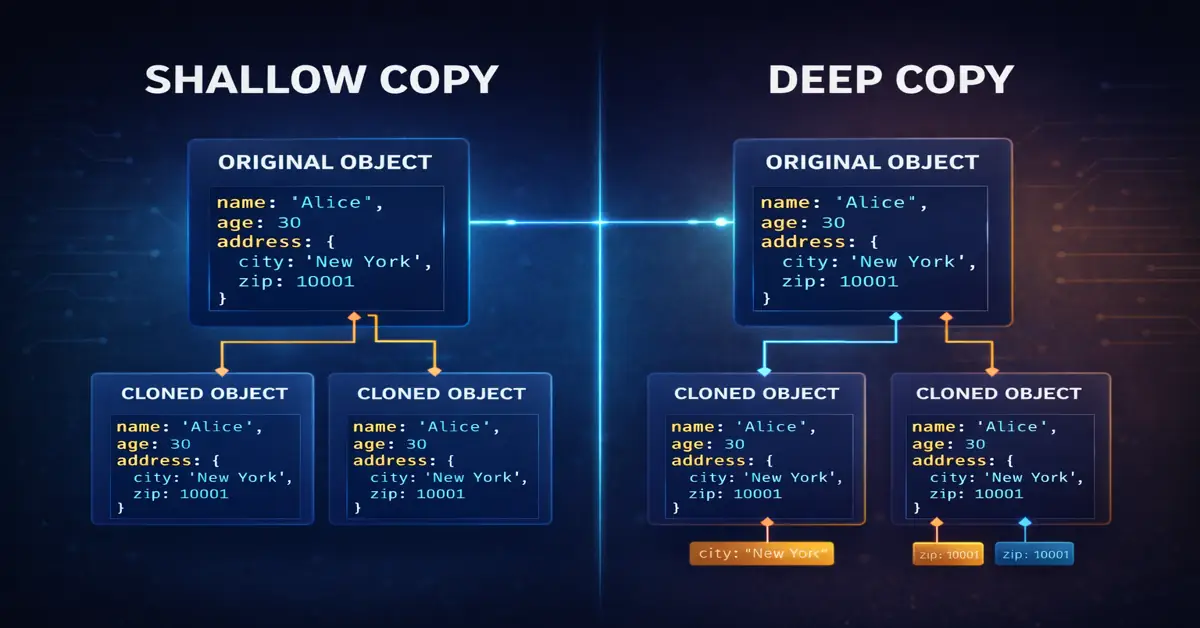
What Is a Shallow Copy?
A shallow copy creates a new object, but it copies references of nested objects instead of duplicating them.
This means:
- Top-level values are copied
- Nested objects still point to the same memory location
A detailed explanation is available on MDN Web Docs.
Example (JavaScript)
const original = { name: "Arsalan", address: { city: "Delhi" } };
const copy = { ...original };
copy.address.city = "Mumbai";
console.log(original.address.city); // Mumbai
What Is a Deep Copy?
A deep copy creates a completely independent copy of an object, including all nested objects.
This means:
- No shared references
- Changes in the copy do not affect the original
A conceptual overview can be found on GeeksforGeeks.
Example (JavaScript)
const original = { name: "Arsalan", address: { city: "Delhi" } };
const copy = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(original));
copy.address.city = "Mumbai";
console.log(original.address.city); // Delhi
Shallow vs Deep Copy: Comparison Table
| Aspect | Shallow Copy | Deep Copy |
|---|---|---|
| Nested Objects | Shared reference | Fully duplicated |
| Memory Usage | Low | High |
| Performance | Faster | Slower |
| Data Safety | Risk of mutation | Safe |
| Use Case | Simple objects | Complex objects |
Common Ways to Create Shallow Copy
JavaScript
- Spread operator (
{ ...obj }) Object.assign()Array.prototype.slice()
Common Ways to Create Deep Copy
JavaScript
JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(obj))(limitations apply)structuredClone()(modern browsers)- Utility libraries like Lodash
Details on structuredClone() are explained on MDN.
Performance Considerations
- Shallow copy is faster and uses less memory
- Deep copy can be expensive for large or deeply nested objects
- Choose based on data size and mutation risk
Real-World Use Cases
When to Use Shallow Copy
- State updates with immutable patterns
- Objects without nested structures
- Performance-critical code
When to Use Deep Copy
- Configuration objects
- Data isolation between modules
- Avoiding side effects in complex systems
FAQs
Is deep copy always better than shallow copy?
No. Deep copy is safer but slower and memory-intensive.
Does spread operator create deep copy?
No. It creates a shallow copy only.
Is JSON-based deep copy reliable?
It fails for functions, undefined, Date, Map, Set, and circular references.
What is the best deep copy method in JavaScript?
structuredClone() is the safest modern solution when available.
Conclusion
Shallow copy and deep copy serve different purposes. Shallow copy offers speed and efficiency, while deep copy provides safety and isolation. Understanding the difference is critical for writing predictable and bug-free code.